What is a chatbot?
A chatbot is a program or application that users can converse with using voice or text. You may have used a chatbot for sales or customer service support online. The bots simulate human conversation and attempt to answer your queries before passing you on to a human representative.
Chatbots were first developed in the 1960s, and the technology powering them has changed over time. Chatbots traditionally use predefined rules to converse with users and provide scripted answers. Contemporary chatbots use natural language processing (NLP) to understand users and can respond to complex questions with great depth and accuracy. Your organization can use chatbots to scale, personalize, and improve communication in everything from customer service workflows to DevOps management.

What are the benefits of chatbots?
Chatbots can search and retrieve information from any internal or external knowledge base and provide answers through human-like conversation.
Efficiency through automation
Chatbots save time and effort for an organization. They combine the steps of complex processes to automate repetitive tasks through a few simple voice or text requests. You can address common issues automatically and scale operations as needed.
Flexibility
You can build chatbots that respond to either voice or text in users' native languages. You can embed customized chatbots in everyday workflows to engage with your employee workforce or consumer engagements. Customer service chatbots can respond to customer queries on social media channels, websites, and messaging applications. Similarly, you can set them up to respond to employee queries on any internal application.
Broader customer engagement
A good customer experience can help your organization stand out. Customer service that relies exclusively on human interaction has limited capacity and lacks flexibility. With customer service chatbot software, your organization can personalize customer interactions at scale. You can reach them in familiar environments, respond to their requests faster, and meet their expectations. You can be proactive and customize your outreach.
What are use cases for chatbots?
Organizations across industries use chatbots to streamline the customer experience, increase operational efficiency, and reduce costs.
Enterprise productivity
You can integrate chatbots with enterprise backend systems such as customer relationship management (CRM), inventory management programs, or human resources (HR) systems. They can check sales numbers or inventory status, generate marketing reports, or assist with employee orientation.
Read about how Infor uses AI in its enterprise
Personal assistants
Chatbots can simplify and expedite everyday personal activities. For example, customers can order new shoes or groceries, book medical appointments, or make travel reservations from their mobile devices, browsers, or favorite chat platforms.
Read about Kelley Blue Book's chatbot for car owners
Call center applications
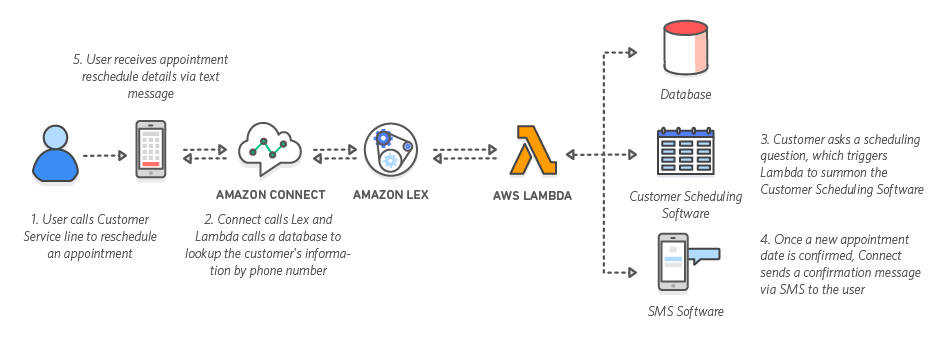
Chatbots can help solve customer requests in a call center application and decrease employee workload. For example, customers could converse with a chatbot to change passwords, request a balance on an account, or schedule an appointment. Customer service bots can maintain context and manage the dialogue. They can also dynamically change their responses based on the conversation so you can exceed customer expectations.
Learn about Amazon Lex chatbots in Amazon Connect call centers
What are the types of chatbots?
Chatbots extract speech elements and provide instant responses to replicate human conversation. Over time, the technology powering chatbots has evolved.
Rule-based chatbots
Rules-based chatbot technology is the simplest version of chatbot software. It provides users with buttons or menus to seek specific information. Users go through a series of steps and predetermined questions to solve their problems. They cannot type a question but only click on one from a predetermined question set. The chatbot has a built-in dictionary that maps a specific response to every question. It gives the same response to all users who ask a specific question.
Rule-based chatbots aren't good options for scenarios that involve multiple unknown factors. They're also difficult to scale and can take longer than desired to answer the user's requests.
Keyword-based chatbots
Keyword-based or declarative chatbots extract specific keywords from conversations and provide corresponding responses. They use keyword recognition techniques to extract the intent, subject, and sentiment from the questions and respond using scripted replies in predetermined ways.
For example, if you enter "How do I activate my account?" the chatbot detects “activate my account” as the keywords and responds with a step-by-step guide.
Keyword-based chatbots are still limited in their responses and operate only within the scope of topics that have been preprogrammed.
AI-powered chatbots
Recent artificial intelligence (AI) technologies have expanded what a chatbot can do.
For example, contemporary chatbots can provide dynamic responses to customers instead of scripted replies. To achieve this, chatbots use natural language processing (NLP), natural language understanding (NLU), and natural language generation (NLG).
Generative AI has also made chatbots more capable. A chatbot can be powered by a large language model (LLM), pre-trained on large volumes of human language data. These models help chatbots simulate natural conversation.
Generative AI-powered chatbots can also handle complex questions and accurately detect sarcasm, sentiment, and subtle conversation variations. For example, a customer could ask, “I know it's peak hour, but how soon can I get my food?" The chatbot would then give a natural, precise response. Chatbots powered by generative AI can switch seamlessly between topics and respond sensitively or with humor.
What are other technologies related to chatbots?
There are many technologies related to chatbots that have distinct meanings.
Virtual agent
A virtual agent, or virtual assistant, is an intelligent computer program that converses with customers naturally and helps them resolve problems. Virtual assistants can understand emotional nuances, intent, and contextual relevance in conversations. Any AI-powered chatbot can be a virtual assistant if required, but rule-based chatbots can't be.
Conversational AI
Conversational AI is an umbrella term that refers to any AI that communicates with users through text or audio. For example, both Amazon Ask, a chat-based assistant, and Amazon Alexa, a voice assistant, are forms of conversational AI. Many chatbots use conversational AI.
Voicebot
A voicebot, or voice assistant, is a chatbot that listens to voice commands, performs specific actions, or replies to users in natural speech. For example, Alexa is a voice assistant that performs various tasks, such as controlling smart home devices, reporting weather, and playing music.
Voice assistants use automatic speech recognition (ASR) along with other AI technologies used by chatbots. With ASR, voice assistants can analyze complex speech patterns and provide seamless, voice-enabled user experiences.
Chatbot Software
Chatbot software refers to a specialized platform or tool enabling businesses to build, deploy, and manage chatbots. Chatbots are AI-powered virtual assistants designed to interact with users in natural language, simulating human-like conversations. They can be integrated into various communication channels such as websites, messaging apps, social media platforms, and voice assistants.
What chatbot software is available in AWS Marketplace?
With your AWS Account, you can explore thousands of solutions from AWS Partners. AWS Marketplace offers chatbot software solutions to support your unique use case. Some of the most popular solutions include Cyara Enablement Services, eGain for Amazon Connect, Talk Desk, Calabrio ONE, Verint Open Platform, and Genesys. Implementing chatbot software brings numerous benefits to businesses. Let's explore some of the key advantages:
Improved customer service and support
Chatbot software significantly improves customer service and support by providing instant assistance and quick response times. Customers can engage with chatbots at any time, eliminating the need to wait for a human agent's availability. Chatbots can simultaneously handle a high volume of inquiries, ensuring that customers receive prompt attention and support. With their ability to understand natural language and provide accurate responses, chatbots offer consistent and reliable support, reducing customer frustration and enhancing satisfaction levels.
Increased efficiency and cost savings
Chatbots automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks, increasing operational efficiency and cost savings. They can handle routine inquiries, perform simple transactions, and guide users through self-service processes, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex and critical tasks. Chatbots can handle many interactions simultaneously, reducing the need for additional customer service representatives. This scalability and efficiency result in business cost savings, as they can handle more inquiries with fewer resources.
24/7 availability and instant response
One of the significant advantages of chatbot software is its ability to provide 24/7 availability and instant responses. Customers can engage with chatbots anytime, including outside regular business hours. This round-the-clock availability ensures that customers receive support and information whenever needed, regardless of their time zone or location. Instant response times also contribute to a positive customer experience, as customers do not have to wait for a human agent's availability, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Personalized customer experiences
Chatbot software allows businesses to deliver personalized customer experiences at scale. By leveraging user data and preferences, chatbots can provide tailored recommendations, personalized product suggestions, and customized responses based on individual customer needs and interests. Chatbots can access customer profiles, order history, and browsing behavior to offer relevant and personalized interactions. This personalization enhances customer engagement, fosters loyalty, and creates a more personalized and human-like user experience.
How do organizations build AI chatbots?
How to make a chatbot? Organizations can build AI chatbot software in three ways depending on the use case.
Build your own LLM
Some organizations build their own large language model (LLM) on the datasets of their choice. While this approach gives the most control, it is computationally intensive, extremely expensive, and time-consuming. It is best suited for very large organizations that want to use the LLM for applications beyond chatbots.
Customize an existing LLM
Organizations customize an existing LLM for their use case, including specific data and internal knowledge bases. Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) is the primary technique to enhance the LLM. RAG introduces an information retrieval component that utilizes user input to pull information from a new data source. The user query and the relevant information are both given to the LLM. The LLM can reference custom data and respond with full AI capabilities,
Guidance for high-speed RAG chatbots on AWS >>

Use a fully managed service
Organizations that quickly want to add a conversational interface to an existing application like a booking system prefer using a fully managed service. You identify a set of actions or intents that you want your bot to fulfill. For example, a ticket booking bot can have intents (tasks it can perform) to make, cancel, and review reservations. You also identify phrases that invoke intent, such as, “Can I make a reservation?” If your bot needs more data input, you can define prompts the bot should ask to collect information— for example, “What show time would you like to reserve?” The service manages all the internal deep learning technology so you can focus on your business requirements.
What are the best practices in building chatbots?
Creating a chatbot that meets customer expectations and aligns with your business goals requires attention to best practices.
Transparency
For transparency, let customers know when interacting with an AI-powered chatbot. Disclosure sets clear expectations, enhances satisfaction, and improves the customer experience. You can promote customer trust and increase acceptance of conversational chatbots.
Integrations
Efficient, instant responses are central to a successful chatbot. Integrate your knowledge base to give your chatbot immediate access to relevant information. Connect it to other backend systems like CRM or ERP to respond with personalized information based on a customer’s interaction history or account details. That way, your chatbot can address common queries accurately, reduce response time, and improve user satisfaction.
Test and improve
A chatbot requires ongoing testing to ensure it’s meeting performance standards. Implement automation to monitor the chatbot’s interactions to ensure compliance with service guidelines. Use insights from customer feedback to optimize chatbot interactions and expand its use. Insights also allow you to develop new use cases, support additional languages, and improve service across different channels. This data-driven approach ensures your chatbot remains relevant and meets current customer needs.
How does AWS help with building chatbots?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers many options to help you build chatbots or other conversational AI.
AWS Trainium is the machine learning (ML) chip that AWS purpose-built for training your own LLM. Each Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) Trn1 instance deploys up to 16 Trainium accelerators. This delivers a high-performance, low-cost solution for LLM training in the cloud.
Amazon Bedrock is a fully managed service that offers a choice of customized LLMs and a broad set of capabilities to build generative AI applications. Using Amazon Bedrock, you can easily experiment with and evaluate top LLMs for your use case. You can privately customize them with your data using RAG and build the AI chatbots you need.
Amazon Lex is a fully managed service that builds conversational interfaces using voice and text. Powered by the same conversational engine as Alexa, Amazon Lex provides high-quality speech recognition and language understanding capabilities. You can add sophisticated conversational AI to new and existing applications with Amazon Lex.
Get started with chatbots and conversational AI on AWS by creating an account today.






