What is a Public Cloud?
A public cloud is a cloud computing model where IT infrastructure like servers, networking, and storage resources are offered as virtual resources accessible over the internet. Traditionally, organizations had to purchase and self-manage the infrastructure required to run applications. It was costly to set up and maintain, and advanced computing capabilities remained beyond the reach of many organizations. The public cloud solved these challenges by making IT resources accessible as fully managed services.
A third-party provider maintains the hardware, relevant software, and licenses in a globally distributed network of data centers. You can access exactly what you need on-demand and at any scale from any device of choice. Your organization can use the public cloud to access cutting-edge and emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) services, blockchain, and Internet of Things (IoT). This increases the speed and adoption of technological advances and improves service delivery and customer satisfaction.
What are the benefits of the public cloud?
Public cloud service providers can help you meet various needs, from simple web hosting to complex machine learning applications. With a public cloud, you get benefits like these.
Scalability
Public clouds offer virtually unlimited scalability. You can quickly increase or decrease resource usage based on demand without worrying about running out of capacity. You can deploy services closer to your end users from public cloud data centers worldwide. This offers better performance even at scale.
Cost efficiency
Public clouds operate on a pay-as-you-go model. Instead of investing heavily upfront in hardware and infrastructure, you pay only for the resources you use. This can lead to significant cost savings. Different pricing models like free tier and save when you commit allow your organization to optimize costs further.
Faster time to market
The cloud service provider is responsible for infrastructure maintenance, updates, and patching. So, your IT teams can focus on value-added activities instead of routine maintenance tasks. Your developers can prioritize experimentation and solution development to meet customer requirements more efficiently. They can utilize the latest technologies without researching, buying, and setting up the infrastructure.
With prebuilt services and tools, you can deploy new applications and services in a fraction of the time it would take with traditional methods.
Reliability
Your public cloud provider invests heavily in infrastructure and maintains multiple data centers worldwide. You get access to the latest hardware and software as third-party providers ensure all upgrades and patches are up-to-date. You can also access automatic backup and disaster recovery solutions, which helps ensure data resilience. You get high availability and reliability from automatic redundancy coupled with technologies like content delivery networks and load balancers.
Sustainability
Public cloud service providers use economies of scale to optimize energy use and have the capital to invest in renewable energy sources. They can focus on energy efficiency across all aspects of their cloud infrastructure, from data center design and hardware selection to performance modeling for continuous improvement. Businesses can reduce their carbon footprint by utilizing shared resources in a public cloud. Your cloud service provider may also offer tools and resources to monitor the environmental impact of your cloud services usage and reduce your environmental footprint.
How does the public cloud work?
The public cloud operates by leasing computing services over the internet, based on a multi-tenant model where multiple users share the same resources. It includes many different technologies that abstract the complexities of IT resource management. As a user, you can handle your infrastructure as code.
We give an overview of some key aspects of public cloud computing next.
Data centers
Public cloud providers have vast networks of physical data centers spread across the globe. The data centers house the physical hardware and software tools—like servers, storage devices, and network equipment—that support public cloud services. The cloud provider monitors its data centers to detect and resolve issues proactively.
Virtualization
At the core of the cloud's flexibility and scalability is virtualization technology. It allows a single physical resource to be distributed as multiple virtual resources to different users. For example, the public cloud provider can run multiple virtual servers or instances on a single physical resource. Every cloud instance contains its own applications and operating system.
Resource pooling
Cloud providers pool resources such as storage and processing power to serve multiple customers. Resources are dynamically assigned and reassigned according to demand. You can monitor and record the usage of services, which is crucial for billing purposes. As customer, you pay for what you use, similarly to how utilities like electricity work.
API integration
Cloud providers offer APIs that developers can use to integrate the cloud's capabilities into their applications. APIs enable tasks like automating resource provisioning or collecting usage metrics. They allow users to integrate functionality beyond the computing resources of their organization.
For example, machine learning (ML) algorithms require many high-performance servers to set up and self-manage. Instead, you can access ML functionality through APIs of cloud-based services that run in the public cloud environment.
Service agreements
Public cloud providers offer service level agreements (SLAs) that guarantee a certain level of service, uptime, and performance. The SLAs outline details of common metrics so you can meet your service level objectives when using the public cloud. The SLAs ensure reliability and performance so public cloud users can confidently plan their application and data storage architecture.
What's the difference between private cloud, hybrid cloud, and public cloud?
Hybrid, public, and private clouds are different cloud computing models. We break down some of their distinctions next.
Private cloud
In a private cloud, a single organization controls and maintains the underlying infrastructure to deliver the IT resources. Consider an organization with several departments, like finance and marketing, that need computing resources for their software applications. In a private cloud setup, the organization purchases server hardware, maintains it in a central data center, and delivers the resources to the different departments over a network. Individual teams may additionally invest in software infrastructure like operating systems or database software for their applications.
Private cloud vs. public cloud
Before Amazon introduced cloud services, most companies purchased and maintained hardware in their internal on-premises data centers or co-location facilities to support IT operations. After Amazon Web Services (AWS) launched, companies attempted to replicate the cloud computing model on their internal infrastructure. The term private cloud was introduced to distinguish between these internal cloud environments and third-party, public cloud services provided by organizations like us.
Today, some companies have adopted technologies and changes in their operations to offer a selection of the cloud computing concepts. One example is that companies can charge their business units for the private cloud services that they use. However, for the most part, customers have not truly succeeded in deploying a private cloud with benefits comparable to the public cloud. You can read more about our in-depth public cloud vs. private cloud comparison.
Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud is a setup where a company uses both the public and private cloud. It is an IT infrastructure design that integrates a company’s internal IT resources with third-party cloud provider infrastructure and services. With a hybrid cloud, you can store your data and run your applications across multiple environments.
Hybrid cloud vs. public cloud
Organizations typically adopt hybrid cloud strategies to overcome private cloud limitations. They want to continue using their existing on-premises data center and still access the public cloud as needed. Hybrid cloud offerings let you seamlessly switch workloads between different environments. For instance, when organizations run out of computing resources in their internal data center, they burst the extra workload to external third-party cloud services. Cloud bursting is a convenient and cost-effective way to support workloads with varying demand patterns and seasonal spikes in activity.
What are the security considerations in the public cloud?
Public cloud services are designed to meet the highest data protection and security requirements. For example, world-class security experts monitor AWS infrastructure and build and maintain our security services. To aid your compliance efforts, AWS regularly achieves third-party validation for thousands of global compliance requirements. We continually monitor compliance demands to help you meet security standards for finance, retail, healthcare, government, and beyond. You always own your data, including the ability to encrypt it, move it, and manage retention.
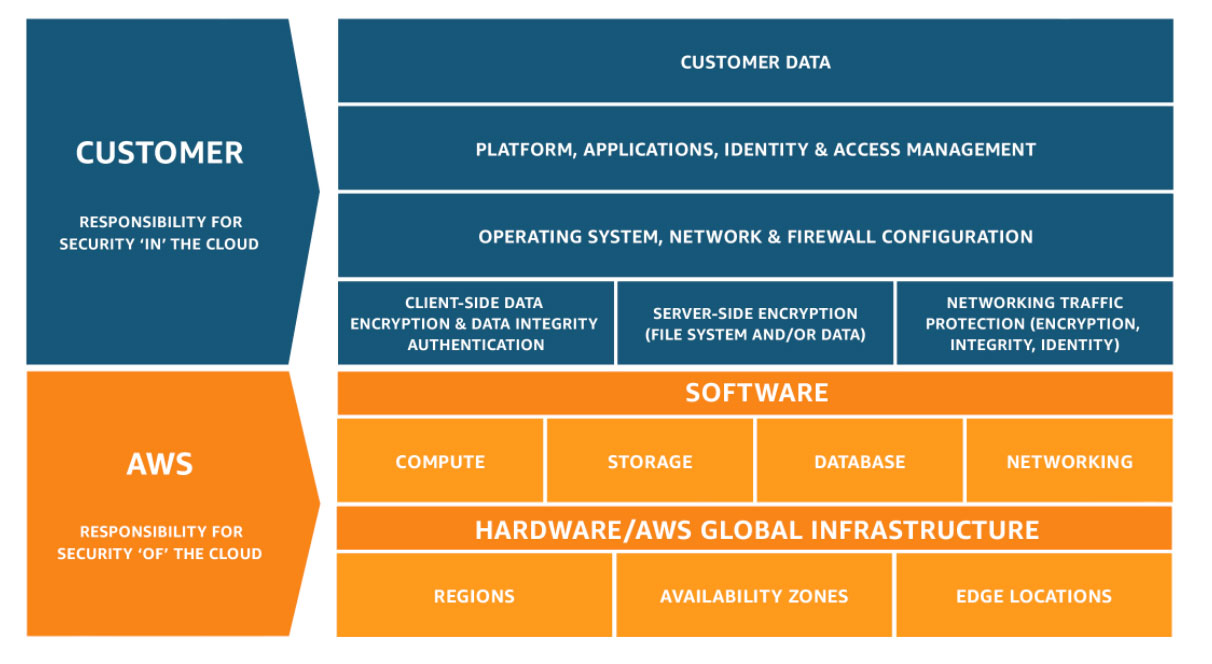
Having said that, it is important to note that public cloud security follows a shared responsibility model. The public cloud provider is responsible for the security of the cloud. They protect the infrastructure that runs all of the services offered in the cloud. At the same time, the customer is responsible for security in the cloud. Customer responsibility is determined by the public cloud service the customer chooses. The service determines the amount of configuration work the customer must perform as part of their data security measures. Some cloud computing services offer greater control and customizability but also increase the customer's security responsibility.
How can AWS support your public cloud requirements?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers more than 200 fully featured services from data centers globally. Millions of customers—including the fastest-growing start-ups, largest enterprises, and leading government agencies—use AWS to lower costs, become more agile, and innovate faster. We are continuously innovating the design and systems of our data centers to protect them from man-made and natural risks.
For example, with AWS as your public cloud provider, you get the following benefits:
- Significantly more services, and more features within those services, than any other cloud provider.
- Fully managed services for categories like compute, storage, databases, analytics, artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML), and Internet of Things (IoT). You can build applications for anything you can imagine.
- A flexible and secure cloud computing environment built to satisfy security requirements for the military, global banks, and other high-sensitivity organizations.
Get started with your public cloud on AWS by creating an account today.






